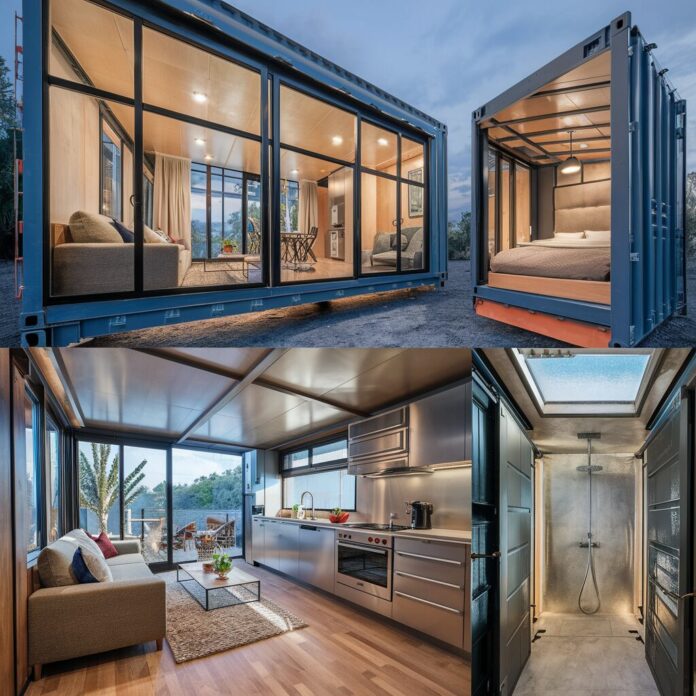
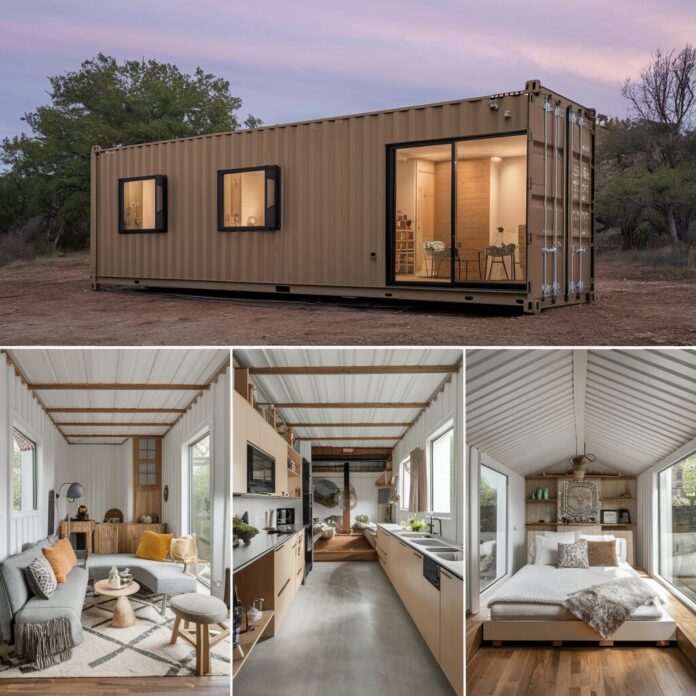
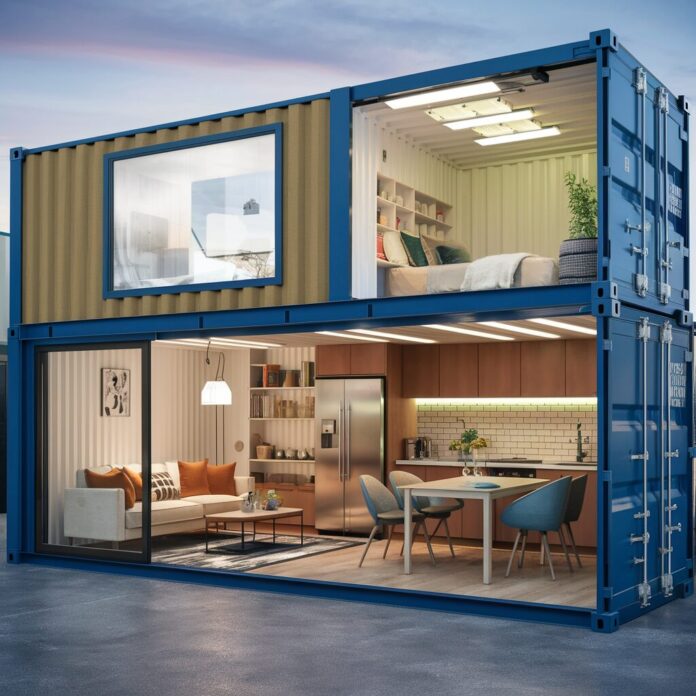
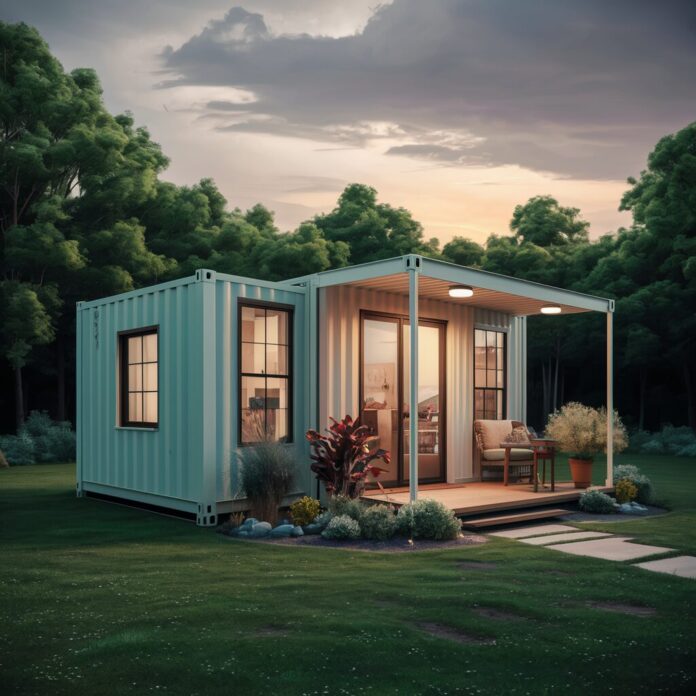
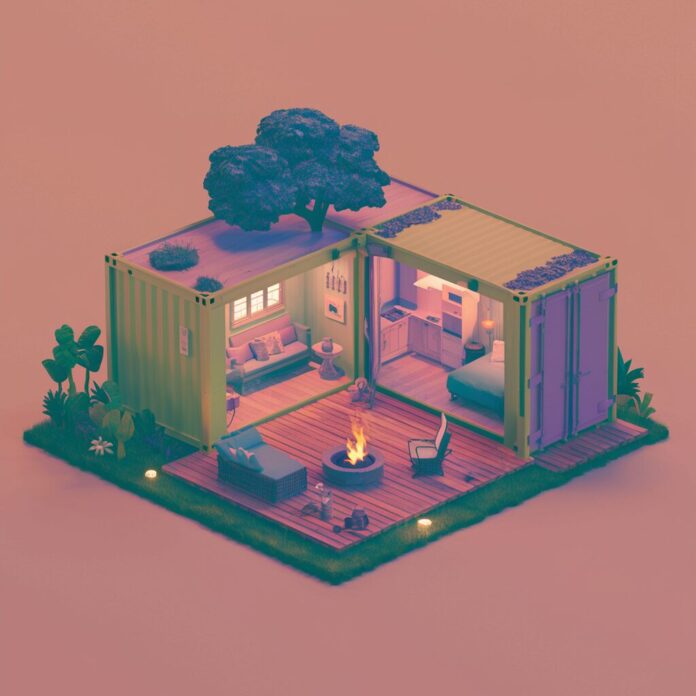
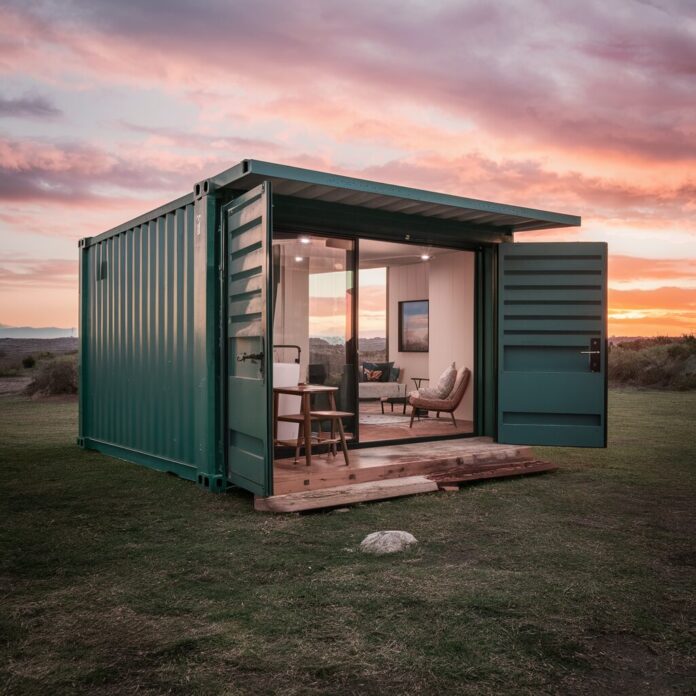
Shipping container homes have surged in popularity as an innovative and sustainable housing solution.
Initially, containers were merely seen as cargo transport units, but today they are being transformed into fully functional and creative residential spaces.
They offer a unique blend of simplicity and modernity, appealing to those seeking an alternative to traditional construction methods.
By repurposing used shipping containers, homeowners can significantly reduce their ecological footprint, making container homes a favored choice among environmentally conscious individuals.
Selecting the Right Container
Selecting the right shipping container is a pivotal first step in creating a container home, demanding careful attention to size, condition, and type to ensure the project’s success.
Finding tiny homes for sale you will find fitting for your needs requires insight into the following factors:
Container Size
Standard shipping containers usually come in two lengths: 20 feet and 40 feet. The 20-foot container offers about 160 square feet of space, ideal for a compact, single-room layout. It is suitable for individuals or couples seeking a minimalist lifestyle.
The 40-foot container, providing approximately 320 square feet of space, is more adaptable for those who need multiple rooms or larger living areas. In addition to length, the container’s height is also important.
Standard containers typically have an interior height of 8 feet 6 inches, but high-cube containers offer an additional foot, bringing the interior height to 9 feet 6 inches, which can significantly enhance the sense of space and comfort.
Container Type
Beyond standard containers, several other types can cater to specific needs:
- High-cube: These are particularly beneficial for those looking to create a more spacious home environment.
- Refrigerated: Known as “reefers,” these are insulated to manage temperature control naturally.
- Open-top: If aiming for designs that include vertical elements like tall windows or even a greenhouse top, open-top containers can be a good choice.
Container Condition
The condition of the container significantly influences the safety, durability, and initial preparation work required:
- New (“One-Trip”): These containers have typically made only one trip by sea.
- Used: These can vary widely in condition. They are less expensive but may come with dents, rust, and wear that require additional work to refurbish.
Choosing a container involves balancing budget constraints with the structural and design needs of the project.
Design Considerations
Effective design is crucial for transforming a compact steel box into a comfortable living space. Detailed architectural planning should focus on the utilization of smart space and reflect the owner’s style.
Integrating large windows and strategically placed skylights can enhance natural lighting and create an illusion of space.
Thoughtful layout planning is essential to maximize the utility of each area within the home, from sleeping quarters to communal spaces, ensuring that the compact environment remains livable and aesthetically pleasing.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Of course, paying attention to legal and regulatory aspects is an absolute must.
Zoning Laws and Building Codes
Navigating zoning laws and building codes is essential for any construction project, including cont
Prospective builders must consult local authorities to ensure their design complies with all regional regulations and obtain the necessary permits before construction begins.
This step is crucial to avoid legal complications that could delay or halt the project.
Safety and Structural Integrity
Maintaining the structural integrity of a shipping container is vital, especially when modifying it with additional doors, and windows, or creating multi-story structures.
A professional assessment is recommended to determine where and how to make cuts in the container without compromising its durability.
Structural reinforcements may be necessary to support modifications and ensure long-term safety.
Modification Processes
Modifying a shipping container involves several structural adjustments, such as cutting openings for doors and windows, which must be done carefully to prevent structural weakening.
Proper techniques and tools are required to avoid rust and corrosion, which can significantly extend the lifespan of the container.
Insulation and Temperature Control
Proper insulation is crucial for making a container home livable, especially in extreme climates. Various insulation materials can be used in this regard, such as:
- Spray foam
- Panels
- Blanket insulation
They depend on the climate and the homeowner’s budget. Also, effective insulation helps reduce energy costs and improve the home’s overall energy efficiency.
Installing Utilities
Electrical and plumbing installations in container homes should ideally be handled by professionals due to the complexity of the tasks.
Proper planning must be carried out to accommodate these systems during the initial design phase to integrate them seamlessly without disrupting the container’s structure.
Interior and Exterior Design
The interior design of a container home can reflect the owner’s personal style and needs.
From minimalist modern aesthetics to cozy traditional interiors, the possibilities are endless.
Multi-functional furniture and built-in storage solutions can enhance the functionality of the space.
Exterior Enhancements
The exterior of a container home can be modified to enhance its appeal and functionality.
Options include different types of paint, cladding materials to improve insulation and aesthetics, and adding external features such as decks, patios, or green roofs, which not only improve the living experience but also help in temperature control.
Budgeting and Cost Management
Effective budgeting and cost management are essential when embarking on the construction of a container home, as this determines not just the feasibility of the project but also its ultimate success. Here’s how to approach budgeting comprehensively:
Initial Costs:
- The cost of the container itself varies widely based on size, condition, and type.
- New or one-trip containers are more expensive, typically costing anywhere from $3,000 to $5,000 each, while used containers can range from $1,000 to $3,000.
- Costs to transport the container to the building site can also add a significant amount to the budget.
Modification Costs:
- This includes cutting openings for doors, and windows, and possibly removing entire sides for larger open spaces.
- Essential for making the container habitable, especially in climates with extreme temperatures.
- Professional installation of plumbing, electrical systems, and HVAC systems are significant expenses.
Finishing Touches:
- Costs here can vary as much as in any traditional home build, depending on the quality and aesthetics of the materials used.
- External paints, cladding, and features such as decks or patios can significantly affect the budget.
Contingency Fund:
- It’s wise to allocate a portion of the budget (typically 10-20%) for unforeseen expenses.
Long-Term Costs:
- Consider the long-term maintenance costs for the type of materials and systems installed.
- Investing in energy-efficient systems, although more costly upfront, can reduce ongoing utility costs.
The Bottom Line
Container homes offer a unique combination of sustainability, affordability, and personalization, making them an excellent choice for future homeowners.
While they come with certain challenges, such as compliance with local laws and the need for structural modifications, the benefits they offer make them a worthwhile investment.