Companies have had differing starts in Silicon Valley when it comes to the idea of startups. This has happened more so in the electric car industry, and there have been varying forms of success for companies both big and small. The same applies to self-driving cars.
One of the success stories is for Tesla, which has already begun the process of selling self-driving cars too with some rudimentary self-driving functions. Another is Google, though they are still in the experiment mode as they test out their cars in selected roads around the country.
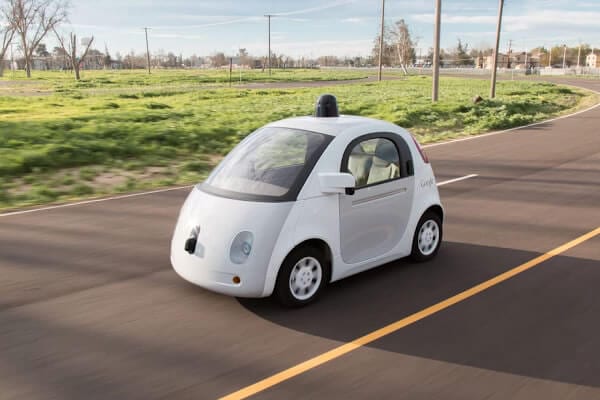
Google initially began the process of self-driving cars back in 2010, and the concept was based on having an emergency driver inside the car who would take over in times of trouble. Google also put a second technician at the time who would help with checking the navigational computer. Google was essentially trying to achieve the same thing that Tesla is trying to do with the AutoPilot feature. This is the idea that Tesla wants to promote with the Model S car, which apparently has handed free technology.
After an experiment that took place in 2013, Google decided to do off with the strict vigilant human approach and decided to let some of its employees take over the car in their daily commutes to work and back home. The results gave engineers insight to one alarming characteristic. They noticed that there was a sharp rise in distracted driving behavior. Christopher Urmson, a former Carnegie Mellon University roboticist who has been directing car project at Google said that the indications made them a little nervous.
It gave them insight and they noticed that it might not be possible for a driver to snap quickly out of what they are doing and take control of the car. Therefore the engineers decided to change tactic. They completely removed the human loop and decided to create a range of cars which did not have brake pedals, accelerators or steering wheels, and it was made not to move at a rate not more than 25 miles per hour. To add protection, a layer of foam was added to the front of the car and a plastic shield was also inserted just in case there were mistakes.
It goes without saying that the car is not suitable for the high-speed interstate trips, but they might be used in urban settings as stop and go taxis.
Google says the car will be probably on the market by 2019. Sebastian Thrun, artificial intelligence researcher who also created the Google project, said that the Google self-driving car team has always been prioritizing safety. He said that their aim was to make the car as safe as it had never been before. As of now, the Google cars can be said to be largely successful.
The largest carmaker in the world, Toyota, is not venturing into the self-driving market. The manufacturer has decided to set up a research center in Palo Alto, California that is aimed at helping drivers when they make errors. The technology is called the ‘guardian angel.’
Tesla introduced its Autopilot system back in October last year, and as expected it was greeted by fanfare. Tesla says that the technology is only to be used in certain cases, and says that there is an issue with the design they call “over trust” issues. This means that humans may not be fully aware of the limitations that might be imposed by the self-driving features. The feature, according to Tesla, is meant to assist drivers and not replace them. It also encourages drivers to be vigilant at all times.