While the Trump administration is more interested in reviving the coal sector in the United States instead of developing the renewable energy sector, the number of residential solar installations continues to grow.
Solar panels can be seen everywhere in the United States today because year after year, the demand for solar power rocketed, which was beneficial for both the environment and homeowners.
Producing clean and free energy using only the power of the Sun is not only beneficial for homeowners by paying less on energy bills, but is also beneficial for the U.S. economy.

The year 2017, when Donald Trump assumed the office (on January 20, 2017), was a declining year for domestic solar in the U.S. after years of continuous growth.
Short history
The Sun’s energy has been used by humankind since antiquity when the Greeks, the Romans and the Chinese used glasses and mirrors to concentrate the sunlight to produce fires.
Scientists started experimenting the photo voltaic effect in the 1800’s, but the first solar cell made of silicon was built in 1954 by scientists at Bell Labs.
The first solar cell got built in 1954 had an efficiency of only 4%, but due to the concentrated work of the scientists to improve the efficiency of the cell, they managed to raise the efficiency at 14% in 1960.
NASA saw great potential in that solar cell and contacted the Bell Labs to create a solar panel that can be used to power satellites.
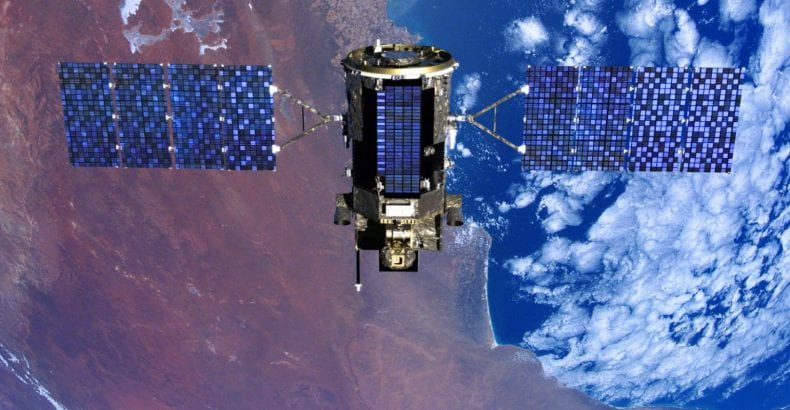

Vanguard 1 was the first satellite launched in 1958 by NASA that used solar energy.
In the 1950’s and 1960’s, solar cells were mostly used by scientists and the space program mainly because the price of the technology was extremely high.
In 1970’s Dr. Elliot Berman and the Exxon corporation designed the first affordable solar cell, which reduced the price of solar from $100 per watt to $25 per watt due to the cheaper materials used in the manufacturing process.
The energy crisis in the 1970’s was a great opportunity for solar energy to prove that it can be used as alternative energy to oil and other fossil fuels.
Solar panels were installed on lighthouses, offshore rigs, railroad crossing and many remote locations.
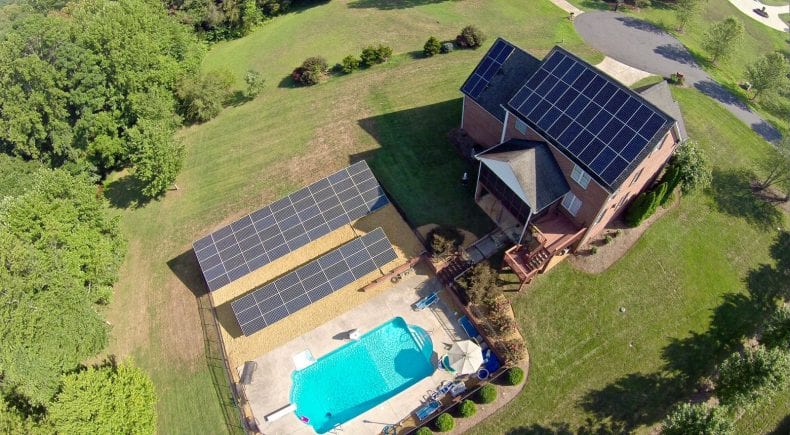

In 1973, the University of Delaware built Solar 1 (the first solar-powered home in the country). In the 1980’s, domestic solar installations slowed down again due to the fact that the price of traditional energy sources dropped again.
The Kyocera corporation created in 1982 a new casting method to produce solar cells on a mass scale, and this method is still the industry standard because it cuts manufacturing costs significantly.
Only in the 1990’s, the governments began to get involved in the R&D (research and development) of solar energy, and they even started to create grants and tax incentives for people that wanted to install and use solar energy systems in their homes.
After this help from the government, and because the manufacturing costs continued to decrease the domestic installations have increased significantly.
The year 2016 was a record year with residential installations of solar energy systems in the U.S. because 15 gigawatts of solar energy were added on a large number of rooftops.

I already mentioned that in 2017, the residential installations of solar PV systems declined in 2017 reaching a value of only 10.6 gigawatts. Alternative Energies posted an article at the end of March 2019, about the best solar batteries for off-grid solar to help the homeowners produce their own clean power and become energy independent while protecting the environment.
The future for residential solar in the U.S.
The year 2019 seems to be the year when residential solar is rising again in the U.S. and the domestic installations of new solar PV systems could reach the level of 15 gigawatts again (repeating the 2016 solar boom).
The trend will be maintained this way by the end of 2025 with an average of 15 gigawatts per year, which will show that residential solar is thriving in the U.S. even in the Trump Era.