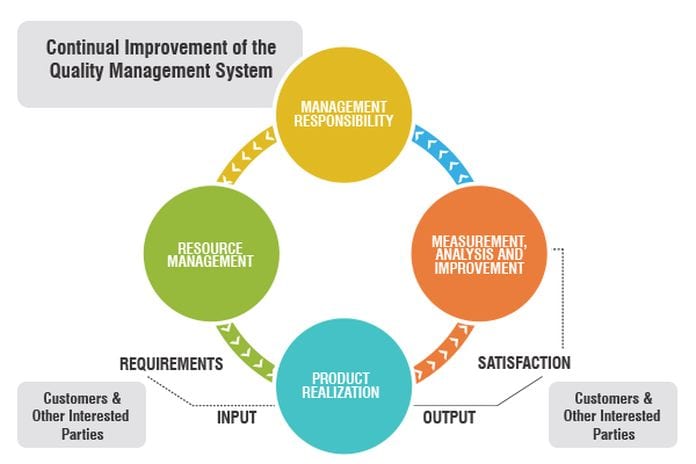
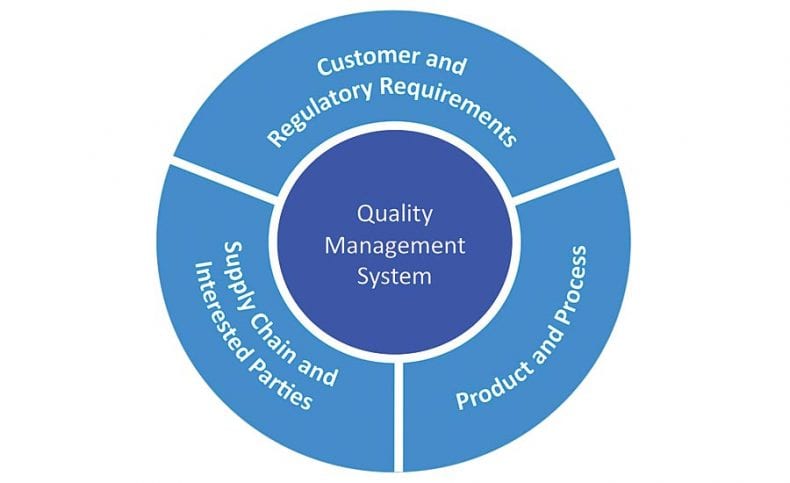
The ISO 13485 standard has been there since long and also characterized quality management system necessities for the medicinal device industry. This standard is commonly acknowledged all through the world as “cutting edge” as for QMS requirements and has regularly been acknowledged as an accepted must for medicinal device organizations with premiums in numerous geographic markets, including Canada and Europe.
The Medical Device Quality Management System Standards ISO 13485:2016 and EN ISO 13485:2016 have been distributed separately in March and April 2016. This started a 3-year progress period, so makers should be in consistence with the new standard by March 2019.
The reexamined ISO 13485 standard is progressively lined up with US FDA 21 CFR section 820 and incorporates different updates, (for example, Medical Device File), refined requirements in configuration control (for example plan check, structure approval, plan exchange), and the expansion of new strategies (for example management Review Procedure). In any case, one of the primary contrasts is the execution of a hazard based methodology for the greater part of the QMS forms. While the idea of a “chance based” QMS is in fact new dialect as for ISO 13845, and quality framework necessities when all is said in done, the desire is that this idea is in arrangement with current translation and industry best practices.
Of specific significance is the “Illumination of Concepts” area of the Introduction to ISO 13485. It incorporates an explanation that says, “when a prerequisite is qualified by the expression ‘where suitable,’ it is esteemed to be proper except if the association can legitimize something else.” This has suggestions for conditions 6 and 8 as far as non-materialism, though in past forms of the standard, just provision 7 could be non-appropriate.
ISO 13485:2016 CHANGES OF NOTE (CLAUSE BY CLAUSE)
Because of the consideration of a few new statements, a few sub-conditions have been renumbered.
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (CLAUSE 4)
Changes to this area principally include:
All procedures that are a piece of a maker’s quality management system will currently should be created utilizing a hazard based methodology.
Basically, surveying dangers reaches out past simply assessing dangers of an item and now incorporates your whole quality management system. Consolidating hazard based basic leadership into the majority of your QMS strategies and procedures is normal.

The distinguishing proof of redistributed procedures and methods for checking. Procedures that are re-appropriated should likewise apply a hazard based reasoning methodology.
There is an expanding pattern of re-appropriating procedures to providers. However, provider the executives has been trying for some, restorative device organizations. The desires characterized in this proviso are progressively unequivocal as for necessities of provider the executives, including applying hazard based methodologies.
Programming utilized as a component of the quality framework must be approved and archived.
Some decipher this has dependably been a necessity of ISO 13485, though one that was unwritten. Primary concern is that any product being used for QMS, just as quality information and records, should be built up, reported, and approved.
Upkeep of a specialized document and device ace record (Medical Device File) for each produced device that incorporates a depiction of the device alongside every single pertinent detail and records.
Once more, the need to keep up a therapeutic device record has dependably been a verifiable prerequisite of ISO 13485. The expansion of this statement incorporates a specialized document and a device ace record—the last of which carries ISO 13485:2016 in closer arrangement with FDA 21 CFR Part 820.

The executives RESPONSIBILITY (CLAUSE 5)
Changes to this area fundamentally include:
Expanded accentuation on administrative requirements.
As noted before, ISO 13485:2003 just made nine references to administrative requirements. Be that as it may, in the previous quite a long while, requirements and desires from administrative bodies has been expanding. These desires lie decisively with the executives inside a restorative device organization.
Documentation of the interrelation of all work force.
Restorative devices have been expanding in unpredictability. Furthermore, the assets and work force are additionally expanding in intricacy. All things considered, guaranteeing the correct assets are recognized, including providers, and their communications could really compare to it ever has been.
Illuminations of existing requirements with respect to quality management system arranging, obligation and specialist, management portrayal and management audit.
A QMS ought to be the core of a therapeutic device organization. A QMS ought to be constantly assessed and checked for suitability and adequacy.
Asset MANAGEMENT (CLAUSE 6)
The standard will presently require device producers:
To characterize the particular abilities and experience required for work force (capability and guaranteeing mindfulness) engaged with the upkeep of the quality management system.
The increments to this statement are putting a heavier accentuation on competency of assets required with an organization’s QMS.
Necessities to keep up frameworks for guaranteeing that staff keep up the essential learning through progressing preparing, just as a component for evaluating the adequacy of such preparing.
Preparing, particularly adequacy of preparing, is of expanding significance. Setting up powerful procedures to guarantee preparing viability is a basic part of a compelling QMS.
To guarantee Infrastructure averts item mistake and guarantees precise treatment of item.
Throughout the years, there have been an excessive number of issues with item mistakes, mislabelling, and item distinguishing proof.
Another provision in this area likewise addresses defilement control issues for clean therapeutic devices, and incorporates requirements identified with the approval of procedures expected to guarantee the honesty and adequacy of sterile device fabricating necessities.
There are a couple of reasons driving this specific change, incorporating increments in device reprocessing. It is likewise an essential perspective for assembling forms relating to clean therapeutic devices.
Item REALIZATION (CLAUSE 7)
The standard will presently require device producers:
To Incorporate hazard management standards in deciding the use of these necessities.
ISO 14971 has been orchestrated since 2007. Notwithstanding, the past rendition of ISO 13485 was in 2003, before this harmonization. ISO 14971 tends to item chance administration all through the whole item lifecycle. Presently ISO 13485:2016 lines up with ISO 14971:2007.
Consolidate new sub-statements in structure and advancement for exchange of plan and improvement yields to assembling.
To some degree shockingly, the requirements of ISO 13485:2003 were non-existent concerning exchange from structure and advancement to assembling. The 2016 form cures this, and in doing as such, better lines up with FDA 21 CFR Part 820.30 directions.
Keep up a structure and improvement document.
ISO 13485:2003 depicted keeping up records of structure and advancement. Notwithstanding, it didn’t unequivocally require a structure and improvement record. This expansion in the 2016 variant is progressively unequivocal and lines up with FDA 21 CFR Part 820.
Guarantee material administrative requirements are met.
As noted above, ISO 13485:2016 has set up expanded unequivocal accentuation on administrative requirements in various zones. Administrative requirements are of uncommon concentration as for item acknowledgment.
Distinguish client preparing required to guarantee the execution and safe utilization of the restorative device.
Expanded accentuation on preparing is common all through ISO 13485:2016. This is additionally the situation with respect to the utilization of medicinal devices, particularly as it identifies with structure and advancement approval.
Build up criteria for assessment and determination of providers including execution and hazard.
While a long-standing practice for most restorative device organizations incorporates characterizing criticality of providers, ISO 13485:2016 is putting considerably more accentuation on guaranteeing your QMS has arrangements set up to address surveying, qualifying, assessing, and observing providers.
Performing provider execution checking as a major aspect of re-assessment process, extra record requirements.
The significance of provider due industriousness and progressing checking is being accentuated.
Guaranteeing obtaining data incorporates, as pertinent item details. Providers to consent to earlier warning of changes.
Is it true that you are seeing a pattern with statement 7? There is an expanded desire on controls with respect to providers all through the whole item acknowledgment process.
Also, overhauling action records must be dissected to decide whether the issue is a protest or be used as an enhancement input.
ISO 13485:2003 was exceptionally broad regarding adjusting. Be that as it may, ISO 13485:2016 tends to the significance of assessing overhauling exercises as client input as well as protests.
Include UDI where required by national or provincial directions.
Interesting device recognizable proof (UDI) is a fresher necessity characterized by FDA and other administrative bodies. The UDI criteria has developed since the 2003 adaptation of ISO 13485.

Include necessities for the approval of the use of PC programming utilized for observing and estimation of requirements.
PC programming utilized for checking and estimation has changed a lot since 2003. Get the job done it to state, PC programming has penetrated our reality in various limits. Thus, PC programming approval is required and expected accordingly.
Estimation, ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT (CLAUSE 8)
Under this area of the overhauled standard, device makers will be relied upon to formalize their procedures for acquiring criticism from both creation and after generation exercises, and to create sound strategies for joining that input into its hazard management program.