Over 3,370,000 diesel automobiles are in use in the United States. These vehicles make up around 43% of all commercial trucks in the country and about 1% of light trucks that are not employed for business reasons. If you are one of the one percent of individuals who purchase a diesel truck for non-commercial reasons, you understand how useful this kind of vehicle is for pulling, pushing, and moving products.
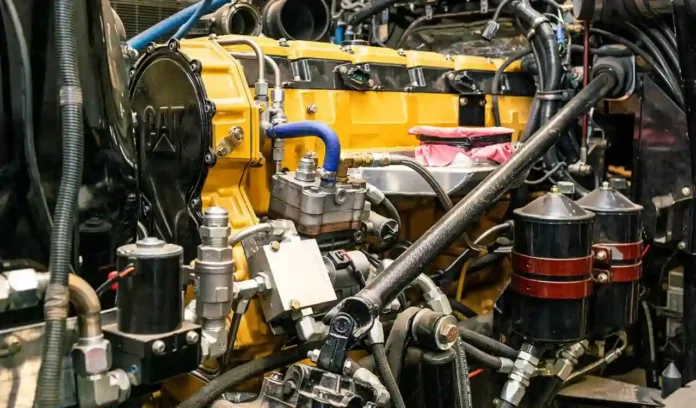
If you want to get the most out of your car, you must keep its engine in good working order. Diesel truck engines are not only durable and long-lasting, but they also need regular maintenance to perform properly.
To prevent expensive repairs on your diesel car and keep it running for many years, follow the engine maintenance guidelines below.
Do Some Research

You must first have a fundamental understanding of your engine before learning some additional information to properly maintain it. If you want to understand more about your specific engine, read the owner’s manual and check for some websites that give information about it. The information you’ve gained here will help you stay on track with maintenance and understand how to properly operate and care for your engine.
Pay Attention to Strange Sights, Smells, and Sounds
You must never ignore unexpected sights, sounds, or smells emerging from your truck. If you observe an excessive amount of noise when you apply the brakes, this may indicate that you need brake repair or replacement. Regardless of the cause of the problem, it is best to contact an expert for assistance in resolving it.
Follow Your Service Schedule
To keep your diesel engine running well, follow the service schedule. Taking this precaution helps to protect your engine from serious damage as it matures. Following your service plan to the letter allows you to identify serious problems and utilize the appropriate IPD engine parts before they become big problems. Your odds of having problems with your automobile decrease in proportion to how well you follow the service schedule.
Take Good Care of the Exhaust System

Your truck’s exhaust system is an important part of the vehicle’s overall performance. Diesel particulate filters (DPF) and diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) systems are being built to fulfill the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) emissions standards.
You should monitor the regeneration of your diesel particulate filter (DPF). This occurs when the particles in the filter reach the point of combustion and are converted into ash and CO2. Regeneration may occur in three unique ways: passively, actively, or via force. If regen occurs often, you should get your car inspected by a service specialist to find the cause. In addition, you should clean your DPF regularly to remove any ash that may have remained after the DPF was regenerated. Finally, ensure that your diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) tank is kept full, since a low-DEF tank may result in error messages and prevent your engine from starting.
Ensure Regular Oil Changes
Changing the oil in your truck’s engine regularly is one of the most critical things you can do to keep it running correctly. Engine oil is the chemical that lubricates the engine’s working parts. However, with time, engine oil may deteriorate and get contaminated with dirt and debris. This may cause significant engine damage, necessitating costly repairs
To avoid this, you should change your truck’s oil every 3,000 to 5,000 miles, depending on the type and model. If you want the finest protection for your engine, buy high-quality oil and filters.
Clean the Filter Element on Time
The air filter element and air inlet pipe are the main components of the engine’s air intake system. The air filter element is advised to be cleaned regularly, although this varies based on the servicing conditions. After three cleanings, it is advised that the air filter element be changed. The air quality in the region where the vehicle is driven often may be used to determine the cleaning cycle. Furthermore, genuine air filter components from high-quality suppliers are required.
Keep Your Diesel Engine Clean

Keeping the engine compartment clean may help prevent problems from happening. Dirt and dust may clog the air filter or enter the oil filter, causing it to malfunction. Use a vacuum cleaner or compressed air to remove any loose dirt from the engine compartment, then wipe down any surfaces that may need cleaning with a sponge or cloth dipped in soapy water.
Save Your Turbocharger from Failing
The flow of oil from the oil pump to the turbocharger is one of the most significant things that happens in a few seconds when you turn on your vehicle. Many events occur in such a brief period. Before you depart, allow your vehicle a few minutes to start and idle before driving out of the parking area. This allows enough time for the engine oil to reach the turbocharger. In other words, starting your car and instantly pressing the gas pedal is the worst thing you can do to a cold engine.
Maintain Your Radiator and Coolant

Keeping in mind that diesel works at a higher temperature than gasoline, it is important to exercise caution and prevent your engine from overheating. Overheating an engine may cause immediate and long-term damage, as well as costly problems that restrict its lifespan.
You should keep your radiator in perfect condition to avoid warping and damaging other engine components. Your truck’s front grill blasts air through it to cool the coolant, which your engine uses to absorb heat. The radiator is likely to wear down over time since it absorbs all of the hot coolant. Every 50,000 miles, we recommend that you do a performance check on your radiator and flush your coolant system fluid.
Drain the Water Separators
Diesel fuel seldom pollutes faster than gasoline, which is one of the key reasons for draining water and debris from a diesel engine. This has the potential to cause corrosion in the system that supplies gasoline. To avoid this problem, many diesel vehicles now have a water separator fitted. The goal of this little filtering device is to remove water from diesel fuel before it reaches engine sections that are more vulnerable to these pollutants.