The Internet is made up of thousands upon thousands of cables, routers and computers and servers. The infrastructure is growing, so is the content. With a few keystrokes on your connected device, you can both play your favorite games easily and smoothly online, check out and order vacation trips, shop for all kinds of goods or play at your favorite online casino.
The internet has really prompted an explosion of online casinos in recent times. Something that is noticeable in the large selection of casinos on the internet. And for all our Dutch gaming fans who are curious and are looking for new online casinos to try, we have the right solution. For more details check Speelhiercasino.com
But in this article, we will not focus so much on gambling, vacation trips or online shopping. Instead, we highlight 9 interesting and important facts about the internet. Facts that can be traced to the birth of the internet to this day.
1. In 1975, two computers communicated for the first time

The experiment took place at the MIT Lincoln Lab, in Lexington, USA. The transfer was slow, but the goal was clear; a more efficient means of communication would be popularized, which would be more popular than both telephones and telegraphs. Now, more than 40 years later, we want to state that their future prophecy was accurate.
2. The first website was uploaded in 1991
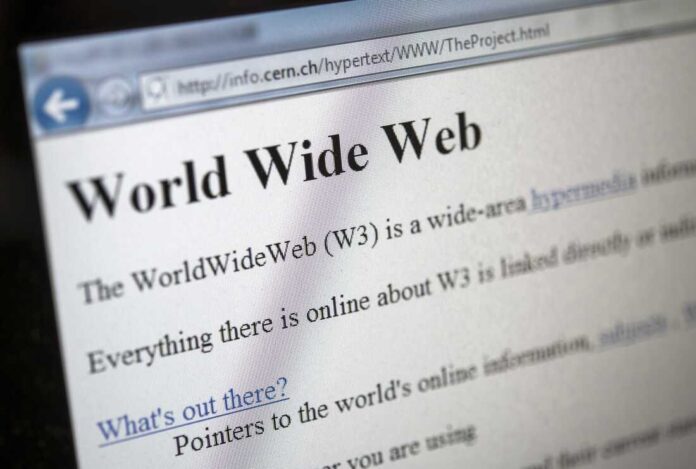
The world’s first website was created in 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee, i.e., the man who invented the web. At the end of the 1990s, at most a “few” million web pages were found on the internet, but today, in 2025, there are over 1.7 billion web pages on the internet.
The majority of these are operated by the American hosting company GoDaddy, which at the time of writing has 17.31% of the market for web hosting. United Layer and AWS Web Hosting (Amazon Web Hosting) are in second and third place, respectively, with their 8.61 and 7.38% of the global market for web solutions.
3. More than half of all people have access to the internet
The Internet became available to private individuals in 1991. 9 years later, in 2000, 361 million people had access to the Internet. Today, global Internet penetration accounts for 57.3%, or 4.33 billion users, World Stats reports. More people should have access to the internet as new infrastructure investments are implemented, we believe.
Of these 4.33 billion users, 2.4 billion are Asians. Europe and Africa come second and third with 651 million and 453 million Internet users, respectively.
Internet use is increasing most in Africa. Partly because the population increase is large, and partly because the internet infrastructure is being expanded and improved at a rapid pace.
4. The average user is connected 6.5 hours / day
According to Bond Cap, the average Internet user spends 6.5 hours a day in front of an Internet-connected device. 91% of those who connect visit e-shops, 84% search for a specific product and 77% buy the product they are looking for.
Just over two hours of daily internet use are used to visit social media sites such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
5. More than 4 billion people can connect

During the third quarter of 2019, 4.33 billion people used the Internet every month. This is an increase corresponding to 8.2% compared to the same period in 2018. An equivalent increase should be relevant for each passing year, according to the same source.
If we look at usage, 90 percent of users use the internet to watch videos and movies, 70 percent of users stream music, 51 percent watch video blogs, 47 percent listen to online radio and 39 percent listen to podcasts.
6. Most of web clients surf by means of portable devices
It’s estimated that about 3.9 billion people, or 51% of the world’s population, connect to the internet every day. And since there are around 5.1 million mobile users worldwide, we can state that over 76% of all telephone users have access to the internet.
50.6% of all internet users connect using a telephone, while 45.5% use a computer and 3.75% a tablet.
The proportion of mobile phone users who can connect with the mobile phone is steadily increasing. From 2018 to 2019, the increase corresponded to 19%.
7. There are many internet users in China

More and more Chinese are connecting to the internet. Although the internet is not completely free due to a huge firewall (“The Great Firewall of China”), the popularity of state-controlled websites is increasing. China’s internet is described as almost as closed as North Korea’s internet, as there is extensive internet censorship.
854 million of China’s approximately 1.4 billion people have access to the Internet, and 99.1 percent of all Chinese Internet users connect using their mobile phones.
The increase is monumental. In 2000, only 22.5 percent of China’s residents had access to the Internet, which means China’s Internet penetration has increased 38-fold in 20 years.
8. How enormous is the web?

There are about 5.5 billion websites online. But only those are visible. There are about 5,000 x this which is the hidden internet, which are temporary pages, closed intranets and “The Dark Web”.
If we calculate the size of the Internet with the maximum transmission capacity in mind, five exabytes (one billion gigabytes) of data flow through the network per day. That transfer rate is equivalent to about 40,000 SD quality movies, per second. In addition, transmission capacity should increase as interest in the Internet grows.
50% of everyone who is online is not human, these are so-called bots that sniff around on various websites and look for information and data.
The internet has grown from being something only the military needed to something we today cannot imagine living without. There are few things that have developed so fast, and so much, like the internet and it is both a little exciting and at the same time a bit scary.
9. How is the internet structured?
The physical part of the internet consists mainly of cables, long and highly efficient ones. The cables ensure that people in many parts of the world can connect to the internet and can be found in numerous cities across the world.
At the time of writing, there are about 300 submarine cables, which are located far below the water surface and extend between entire continents, such as the United States and Europe. The submarine cables are described as forming the backbone of the internet, even though they have the same diameter as a normal garden hose. Inside the submarine cable are thousands of smaller fiber optic cables, which are capable of transporting data at the speed of light.