The 2017 State of DevOps Report revealed that high-performing organizations that have employed DevOps deploy software 46 times more frequently with 440 times faster lead time for changes compared to others. These organizations have also reported a 5 times lower failure rate which in essence, is the true definition of performance. However, performance cannot be separated from performers, as DevOps seeks to bring people, processes, and technology tools on the same page.
The people aspect of DevOps includes seasoned software, IT, and quality engineers with DevOps engineer training from a reputed online training providing institute like Simplilearn and experience, alongside other professionals like business analysts and subject matter experts. Most importantly and this forms part of the core principle of DevOps, is the collaboration between the development and operation teams in the course of software development. While its adoption rate is yet to mature and not all businesses can take advantage of DevOps in their operations, those that have integrated DevOps are already witnessing the remarkable difference that it can bring in the software development process.
Why is DevOps popular
DevOps is first and foremost a culture. This means that the first step to adopting DevOps is creating awareness and common understanding between the development and operations teams as well as other stakeholders so that there is a shift of mindset. In the DevOps culture, everyone owns the process so that greater transparency, collaboration, and communication can be achieved.
DevOps methodology is Agile in nature and features a continuous integration, continuous testing, continuous deployment, and continuous feedback approach to achieve greater efficiency, less waste, and faster delivery of value. Today, nearly all processes run on software. While the complexity of application has been increasing, the market has not relented on its expectations for faster more frequent high-value deliveries. Agile and flexible methodologies like DevOps come as a viable solution to this kind of demand.
Secondly, while DevOps is seen as an end-to-end solution to the efficiency and collaboration challenges, it goes beyond to be at the center of an organization’s profitability, customer satisfaction, and ultimately, overall performance. DevOps is agile. Compared to non-DevOps operations, DevOps will yield four times the productivity of others.
A valuable DevOps feature is the automated configuration in the form of codes controlled by both the development and operations through a single version control tool. This yields consistency in all integrated systems, effective collaboration, and efficiency which facilitates easy scaling without a hefty investment in additional resources.
DevOps also encompasses best practices to enhance security through DevSecOps. According to the DevSecOps philosophy, security should be integrated into every phase of the DevOps lifecycle right from planning and design through to deployment and maintenance.
What is DevOps
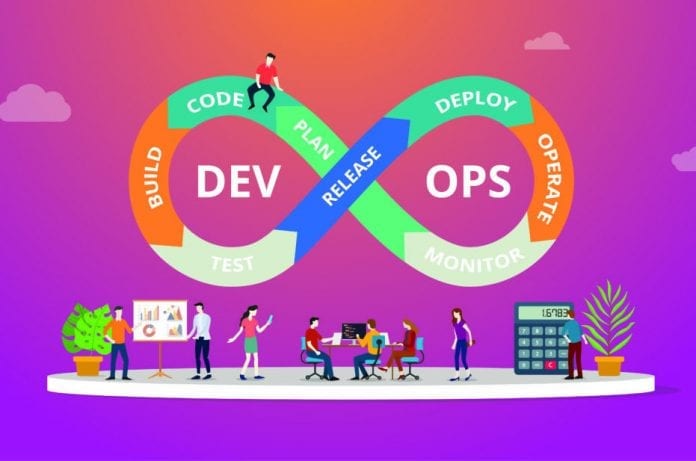
DevOps is a compound term combining development and operations. It refers to the philosophy, culture, and practice that promotes collaboration and communication between the development and operations aspects of software development while at the same time automating the software delivery process and infrastructure changes.
DevOps lays emphasis on communication, departmental, and team collaboration. Its aim is to create a secure automated environment for designing, building, testing, and deploying software fast, frequently, and reliably. This also makes it possible to deploy new features and fix problems within software efficiently.
The benefits that come with integrating DevOps include:
- Shorter time to market
- Higher product quality thanks to standardized processes
- Continuous release and deployment
- Early defect detection
- Collaborative working among development, operations teams, and other business stakeholders
- Team empowerment and innovation
- Greater customer satisfaction
- Increased overall productivity and efficiency
- Stable and reliable operating environments
Phases of DevOps lifecycle
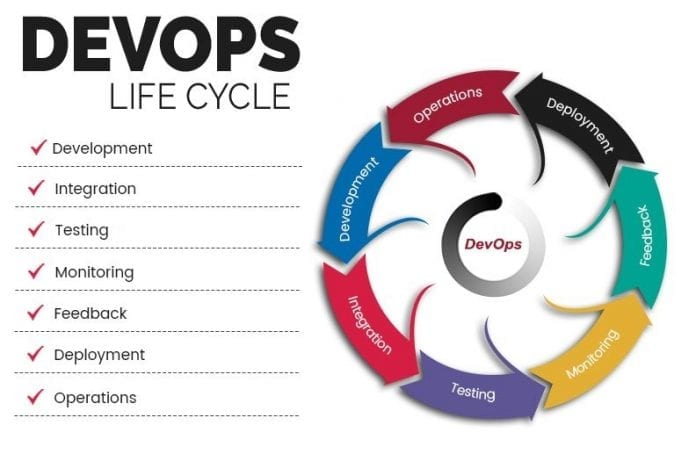
There are 7 key phases in the DevOps lifecycle. These are:-
-
Continuous development
Continuous development involves planning and coding software. In planning, developers try to gain an in-depth understanding of what the project is all about and envision an application that will run the project.
Codes can be built using any of the programming languages and then maintained using a version control tool in a process known as Source Code Management (SCM). Some popular SCM tools include Git, CVS, and Jira. These codes can also be packaged in an executable file for use in the phases that will follow.
-
Continuous integration
This second phase of DevOps is the phase in which the source code gets modified several times in the course of the day or week. Code integration, a very important phase of DevOps in which new functionalities are built and integrated into the existing code. This allows developers to detect bugs early enough.
Code integration also involves code review, unit testing, integration testing, compilation, and packaging in a continuous process which also updates these changes to end-users. A popular tool used in continuous integration is Jenkins.
-
Continuous testing
The developed software is continuously tested for bugs. Developers use tools like Selenium for automation testing, TestNG for report generation, and Docker for simulating the test environment. Automation allows the quality assurance team to run tests on several code-bases concurrently while at the same time generating reports for these tests. This saves them time and errors associated with manual testing and also simplifies the analysis of the failed test cases. After a code has been tested successfully for functionality and is from bugs, it is integrated into the existing code.
-
Continuous monitoring
During continuous monitoring, the operations team tracks the performance of the application. It involves collecting and documenting data on each functionality of the application in a state of continuous operation to identify trends and issues. Issues like low memory, server errors, and other security issues are fixed in this phase. Continuous monitoring is done to keep the application’s optimal function and maintain security.
-
Continuous feedback

The role of the operations team, alongside monitoring the performance of the application, is to evaluate user feedback on its operation to find opportunities for improvement. Every time the source code is updated, the end-user is engaged for continuous testing and feedback on application operation before the next code is integrated. Changes based on user feedback are then updated immediately by the developers.
-
Continuous deployment
In this phase, the final code is deployed into the production pipelines, and deployment should be continuous. Configuration tools like Chef, Ansible, and Puppet together with containerization tools like Docker are used in this phase to facilitate consistent code development, testing, and deployment across all servers.
-
Continuous operations
The final phase in the DevOps lifecycle is a continuous operation. This phase automates the release process along with the updates that will follow. This reduces the time-to-market for the application.
Conclusion
Overall, DevOps is characterized by continuity and automation of processes. This is important as it eliminates challenges that stall the development process. It also significantly reduces the time it takes to detect bugs ultimately delivering high-quality software and improving user-experience.
DevOps adoption continues to rise thanks to this technology breaking down the silos that existed between the development and operations teams. Secondly, it is one of the most reliable technologies for the fast development of high-quality software and has contributed immensely to the evolution of software development. As such certified software engineers are the most sought after in the software development field.









