Ransomware is a significant cybersecurity threat. Hackers use this particular type of malware to encrypt files and demand money to give them back. Annual malware damage exceeds 11 billion dollars. That’s why protecting digital data from ransomware is the top priority. In this article, we’ll take a look at five essential ransomware protection steps you may need to take to keep your data secure. If you want to protect your data, here you can find more information.
Use Strong Passwords

Using secure passwords may seem very obvious, yet it is often neglected. Password protection techniques are well-known for many years, but still, so many people fail to implement them correctly. When an employee registers on your corporate portal, remind the employee about the importance of creating strong passwords.
A right way is simply not letting weak passwords to be created at all. The essential features of firm password policy are:
- The password should be long enough – at least ten characters (more the better).
- Use upper- and lower-case letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Do not use generic passwords like 123456, abcdef, your name, or date of birth.
- Try to create new passwords at least four times a year.
Implement Two-factor Authentication
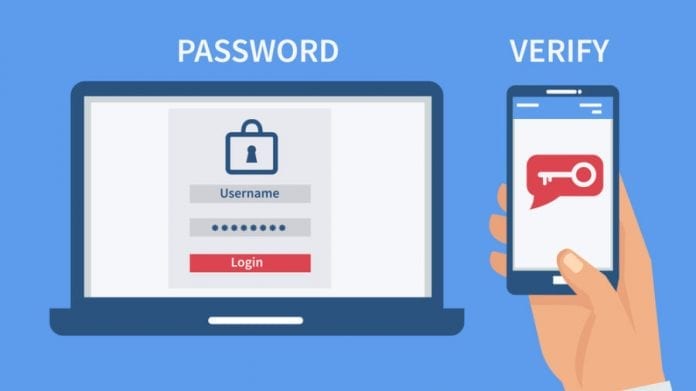
Two-factor authentication (or 2FA) provides the second step of checking whether a user is authorized to enter. 2FA may prove user identity in several different ways. For example, the generation of a unique code by an exclusive app like Google Authenticator. The system can be sent via text message, email, etc.
Having the second check on place dramatically decreases the risk of unauthorized access, and thus limits the malware attacks too. However, it is worth making those two-factor authentication procedures very different, so that a cybercriminal can’t ever get access to both methods.
For example, when using email code as the second step of authentication, you get a risk of finding that some of your employees store their email password and their corporate portal password in the same place. That can let hackers gaining access to these data altogether, passing both methods of authentication and bringing the malware to the corporate network.
Develop and Implement Ransomware Backup Strategy

Backup ensures the safety and reliability of protected data. That’s why choosing a backup solution is extremely important.
The storage of alternate data should be isolated from your leading network so that they remain fully secure even in case the whole system is compromised. Besides isolation and using different types of backup storages (including external storage drives and cloud backups), think about the safety of passwords/keys/credentials you use to access your backups.
For physical backup storage devices, make sure you have a profound policy on who, when, and how you can access the hard drives, how to store them from thefts and physical damage safely.
For cloud-to-cloud backups, you need to carefully choose the alternate providers and make sure you pay on your accounts on time. As the safety of your data is crucial, you need to check the whole backup-restore process to see whether it meets your expectations.
Some backups are better protected from ransomware attacks. The key anti-ransomware alternate features are:
- 1-2-3 strategy
- backup versioning
- high backup frequency
For example, Spinone is one of the cloud-to-cloud alternate solutions that combine 1-2-3 backup plan with storing multiple backup versions and making backup three times a day.
Why is the 1-2-3 strategy so important? That is the method of organizing the data backup securely. The process is based on having 3 data copies stored on two different kinds of media, with at least 1 transcript stored off-site.
Use Additional Anti-ransomware Software

Anti-ransomware tools do a great job of detecting and eliminating ransomware that tries to sneak into networks. Such software is also good at identifying and stopping any programs (that are installed on your devices) when they start to behave suspiciously. For example, when a program tries to make an unauthorized connection to an external server and download a piece of malicious code.
Some ransomware tools, like SpinOne malware protection for G Suite, are designed to give an extra level of security. This tool monitors files for abnormal file behavior to detect ransomware patterns. Moreover, this tool combines the backup features mentioned above with an additional layer of ransomware protection:
- Identification of the damaged (encrypted) files
- Granular recovery from the last successfully backed up version
- Email notifications and detailed reports in case of an attack
Utilizing machine learning algorithms to detect ransomware early is a crucial difference between anti-ransomware tools and backup. After all, backup is aimed just at restoring damaged data but not at repelling malware attack itself.
Arrange Cyber Security Trainings

Last but not least is education. That’s why many companies organize cybersecurity training for employees. The main goal of such training is to give a basic understanding of ransomware threats and ways to combat it. The whole training process consists of many variable topics. However, there are some core ideas that you can encounter in almost all training.
First of all, employees are to be told about malware, its negative impact on businesses, and the ways how ransomware can infect the system.
Secondly, it is essential to address that clicks should not be done automatically: think every time before you click an external link. The same goes for using suspicious devices, installing potentially dangerous apps, or even opening attachments.
Thirdly, all employees should understand that protecting the whole organization is a personal responsibility of each working there. The problem is, even one accidental click from one user may lead to the full-scale infection and cause significant damage to everyone.
However, security training is far from being 100% effective. Employees can only decrease the probability of an attack. On average, any organization has a 33% chance to get malware infection. Security training can help to reduce the chance to 21%, which is still unacceptably high.
To sum up, arranging cybersecurity training is quite an effective measure against malware attacks. However, having the training alone is not enough to keep an organization protected against cyber attacks.